Swing Pricing for Mutual Funds: Breaking the Feedback Loop Between Fire Sales and Fund Runs
Published: August 28, 2018
This paper develops a model of a downward spiral of falling prices and increasing redemptions that can lead to the failure of a mutual fund. It shows how mutual funds can best design swing pricing for effectiveness at preventing runs, even under extreme market stress. (Working Paper no. 18-04)
Abstract
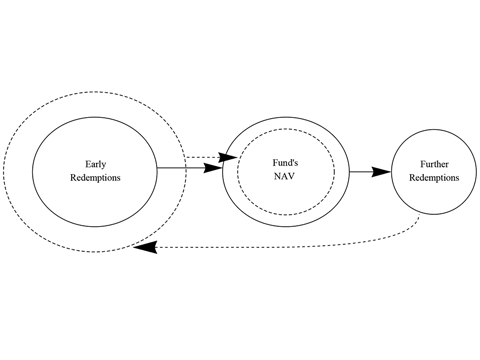
We develop a model of the feedback between mutual fund outflows and asset illiquidity. Alert investors anticipate the impact on a fund’s net asset value (NAV) of other investors’ redemptions and exit first at favorable prices. This first-mover advantage may lead to fund failure through a cycle of falling prices and increasing redemptions. Our analysis shows that (i) the first-mover advantage introduces a nonlinear dependence between a market shock and the aggregate impact of redemptions on the fund’s NAV; (ii) as a consequence, there is a critical magnitude of the shock beyond which a run brings down the fund; (iii) properly designed swing pricing transfers liquidation costs from the fund to redeeming investors and, by removing the nonlinearity stemming from the first-mover advantage, it reduces these costs and prevents fund failure. Achieving these objectives requires a larger swing factor at larger levels of outflows. The swing factor for one fund may also depend on policies followed by other funds.
Keywords: mutual funds, first-mover advantage, swing price, fire sales, financial stability
JEL Codes: G01, G23, G28