Regulatory Arbitrage in Repo Markets
Published: October 29, 2015
This paper documents a pattern of foreign-owned broker-dealers reducing their borrowing in the U.S. triparty repo market, a key source of short-term funding in the financial system, at quarter end and immediately returning to the market when a new quarter begins. This activity reduces their capital requirements under the leverage ratio. (Working Paper no. 15-22)
Abstract
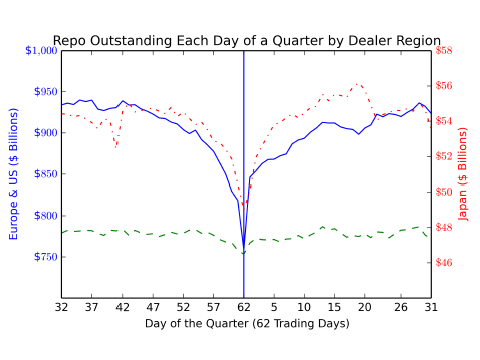
Non-U.S. banks with relatively low capital ratios appear to temporarily remove an average of $170 billion from the U.S. market for tri-party repurchase agreements (repo) before each quarter-end in order to appear safer and less levered. This amount is more than double the $76 billion market-wide drop in tri-party repo during the turmoil of the 2008 financial crisis and represents about 10% of the entire tri-party repo market. Such window dressing-induced deleveraging spills over into agency bond markets and money market funds and affects market liquidity each quarter.